How Computers Really Work | Matthew Justic
P.S. Part names are added by me. Some chapters are merged and renamed.
Part I: Basics
Electrical circuits
| Term | Explanation | Measured in | Water analogy |
|---|---|---|---|
| Electric charge | Causes matter to experience a force | Coulombs | Water |
| Electric current | The flow of charge | Amps | Flow of water through a pipe |
| Voltage | The difference in electric potential between two points | Volts | Water pressure |
| Resistance | A measure of the difficulty for current to flow through a material | Ohms | The width of a pipe |
- Ohm’s Law
- Kirchhoff’s voltage law
The sum of the voltages around a circuit is zero.
Binary
- Analogy v.s. Digital
- Decimal v.s. Binary v.s. Hexadecimal
- Binary data
Text, image, etc.- 8 Bits (b) = 1 Bytes (B)
1 KB = Bytes = Byte
1 MB = Bytes = Bytes
1 GB = Bytes = Bytes
1 TB = Bytes = Bytes
- 8 Bits (b) = 1 Bytes (B)
- Binary logic
ANDORNOTXOR
NAND=NOTAND
NOR=NOTOR
All with associated truth tables to define its behavior
Digital circuits
- Binary representation
- 0 👉 low voltage (Low, LO, off, ground, GND, false, zero, 0)
- 1 👉 high voltage (High, HI, on, V+, true, one, 1)
- Binary logic with transistor
- Transistor
In theory, binary logic can be implemented with mechanical switches. However, it will be much better to control them electrically, rather than mechanically. The leads to the invention of transistor - Logic gate
TheNORgate andNANDgates are known as universal logic gates. With either gate, any logical function can be implemented - Integrated circuit (IC)
- Transistor
- Binary addition
- Adder design
- Half adder
By evaluating the truth table of addition operation, we can design an adder with two logic gates, XOR, and AND. Since we don't deal with carry-out, this is called half adder - Full adder
By combining 2 half adders, we can deal with carry-out - 4-bit adder
Connecting 4 full adder subsequently constructs a 4-bit adder
- Half adder
- Signed numbers
- Negative number representation: two’s complement
Replace every 1 with a 0 and every 0 with a 1 (in other words, flip the bits), and then add 1
Why this represent the negative number? Adding the resulted one with the original one gives you 0
With two's complement, the full adder mentioned before can handle signed numbers' addition without any adaptation
- Negative number representation: two’s complement
- Adder design
Memory and clock signal
- Clock signal
A clock signal alternates its voltage level between high and low. Other components use this signal to work synchronically - Memory
- SR latch
It can be used to store 1 bit of data with two inputs: (S) set as 1 and (R) reset to 0. It can be implemented with 2NORgates - JK flip-flop
Only changes state on clock pulse- T flip-flop
Alternate the state on clock pulse and (T) input
- T flip-flop
- SR latch
Part II: Computer
Computer hardware
- Programmability
- Central processing unit (CPU)
Program instructions reside in memory. The CPU reads these instructions so it can run the program.
- Instruction set
x86, ARM, etc. - Clock
Coordinating the operations. Noted that modern CPU uses pipelining to divide instructions into smaller steps so that portions of multiple instructions can be run in parallel - Core
The parallelism of multicore means that each core works on a different task, a separate set of instructions
- Processor registers
Hold data in CPU during processing - Arithmetic logic unit (ALU)
Logical and mathematical operationsA processor’s ALU is just a complex combinational logic circuit. The ALU’s inputs are values called operands, and a code indicating what operation to perform on those operands.
- Processor control unit
Directs the CPU, communicating with the processor registers, the ALU, and main memoryIt works on a repeating cycle: fetch an instruction from memory, decode it, and execute it.
- Processor registers
- Cache
A CPU first checks L1 for the needed data, then L2, then L3, before finally going to main memory.
- Instruction set
- Random access memory (RAM)
-
Memory address
Computers assign numeric addresses to bytes of memory, and the CPU can read or write to those addresses.
The number of bits used to represent a memory address is a key part of a computer system’s design. It limits the amount of memory that a computer can access, and it impacts how programs deal with memory at a low level.
-
Bus communication
- Address bus
Acts as a selector for the memory address that the CPU wishes to access. For example, if a program wishes to write to address 0x2FE, the CPU writes 0x2FE to the address bus.
- Data bus
Transmits a value read from memory or a value to be written to memory. So if the CPU wishes to write the value 25 to memory, then 25 is written to the data bus. Or if the CPU is reading data from memory, the CPU reads the value from the data bus.
- Control bus
Manages the operations happening over the other two buses. As examples, the CPU uses the control bus to indicate that a write operation is about to happen, or the control bus can carry a signal indicating the status of an operation.
- Address bus
-
- Input/Output
- Memory-mapped I/O (MMIO)
When physical address space is mapped to an I/O device, the CPU can communicate with that device just by reading or writing to its assigned memory address(es)
- Port-mapped I/O (PMIO)
You can think of the set of I/O ports as just another address space, distinct from memory addresses.
- Disk
Hard disk drive (HDD) & solid-state drive (SSD)
- Memory-mapped I/O (MMIO)
Programing language
- Machine code
Example: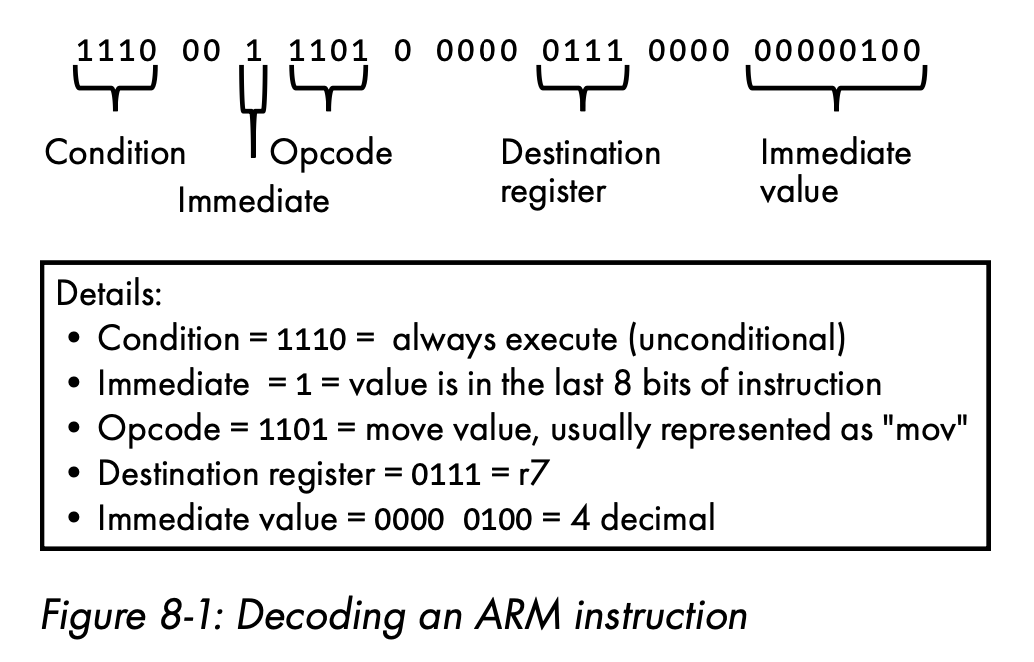
- Assembly language
Human friendly form of machine code that uses human readable notations to represent the binary code - High-level programing
Allow programs to be written in a language that is independent from a specific CPU and is syntactically closer to human language.
- Compiled language e.g. C
- Building software
- Compiler
Source files 👉 object filesA program that converts high-level program statements to machine code for a specific processor.
- Linker
Convert one or more object files into an executable file that the operating system can then run. The linker can also bring in other libraries of compiled code when needed.
- Compiler
- Building software
- Interpreted language e.g. Python
It’s the interpreter’s machine code that actually runs on the CPU.
- Features
Comments, variables, math, logic, program flow, function, object-oriented programming, etc. - Memory access
- Stack memory
Last-in first out (LIFO)The compiler generates code that uses the stack to track the state of a program’s execution and as a place to store local variables... Additional values will continue to be added to the top of the stack until they are no longer needed, at which point they will be removed from the stack.
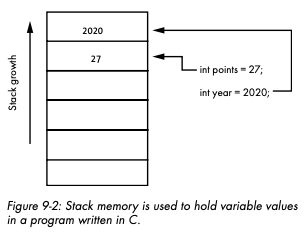
- Stack overflow
- Heap memory
The heap is a pool of memory that’s available to a program. Unlike the stack, heap memory doesn’t work on a LIFO model; there is no standard model for how heap memory is allocated. Whereas stack memory is specific to a thread, allocations made from the heap can be accessed by any of the program’s threads.
- Garbage collection
A memory leak occurs when unused memory isn’t freed.
- Pointer in C
A local variable at an address on the stack that holds the address of an allocation on the heap.
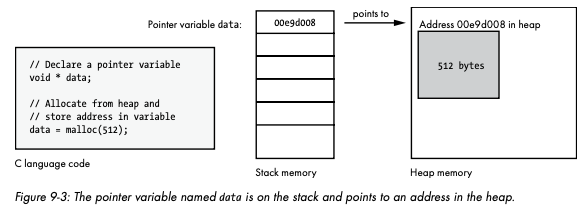
- Garbage collection
- Stack memory
- Compiled language e.g. C
Operating system
- Main stream operating systems (OSs)
- Unix-like OSs
Linux, macOS, iOS, Android - Microsoft Windows
- Unix-like OSs
- Components
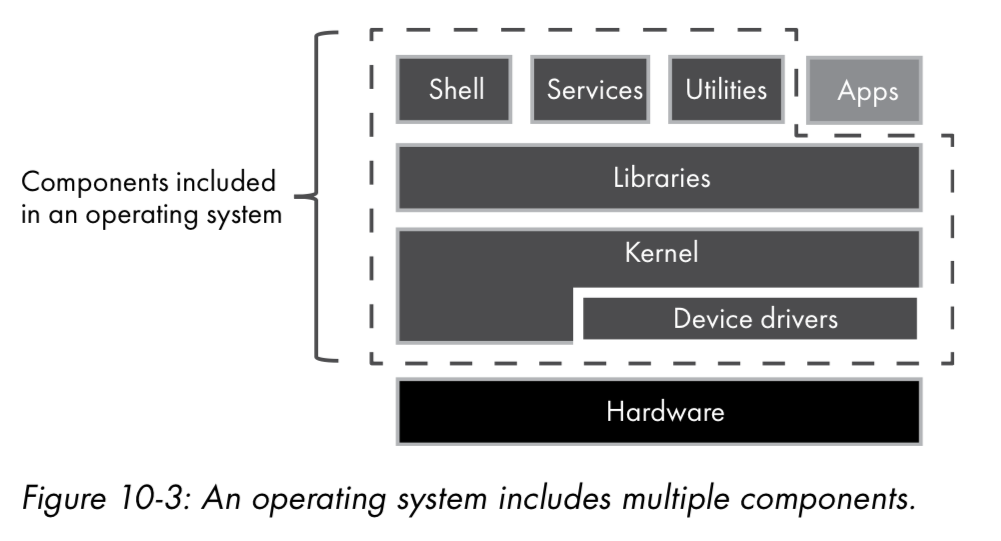
- Kernel
Responsible for managing memory, facilitating device I/O, and providing a set of system services for applications. The kernel allows multiple programs to run in parallel and share hardware resources
- Device driver
A device driver is software that interacts with a hardware device and provides a programmatic interface to that hardware.
- Device driver
- Libraries
Software libraries for developers to build on.
- Application programming interface (API)
Unix-like 👉 Portable Operating System Interface (POSIX)
Windows 👉 WIN16 / WIN32 / WIN64 / Universal Windows Platform (UWP)
macOS 👉 Cocoa
iOS 👉 Cocoa Touch
Android 👉 Android Platform APIs - Application binary interface (ABI)
The source code targets a common API, whereas the compiled code targets an architecture-specific ABI... It’s important that the ABI exposed by OS libraries remains consistent over time. Such consistency allows older programs to continue to run on newer releases of the operating system without needing to be recompiled.
- Application programming interface (API)
- User interface
- Shell
A user interface for working with the kernel.
- Command line interface (CLI)
- Graphical user interface (GUI)
- Daemons (services)
Services running in the background - Utilities
- Applications
- Filesystems
- Shell
- Kernel
- How OS executes code
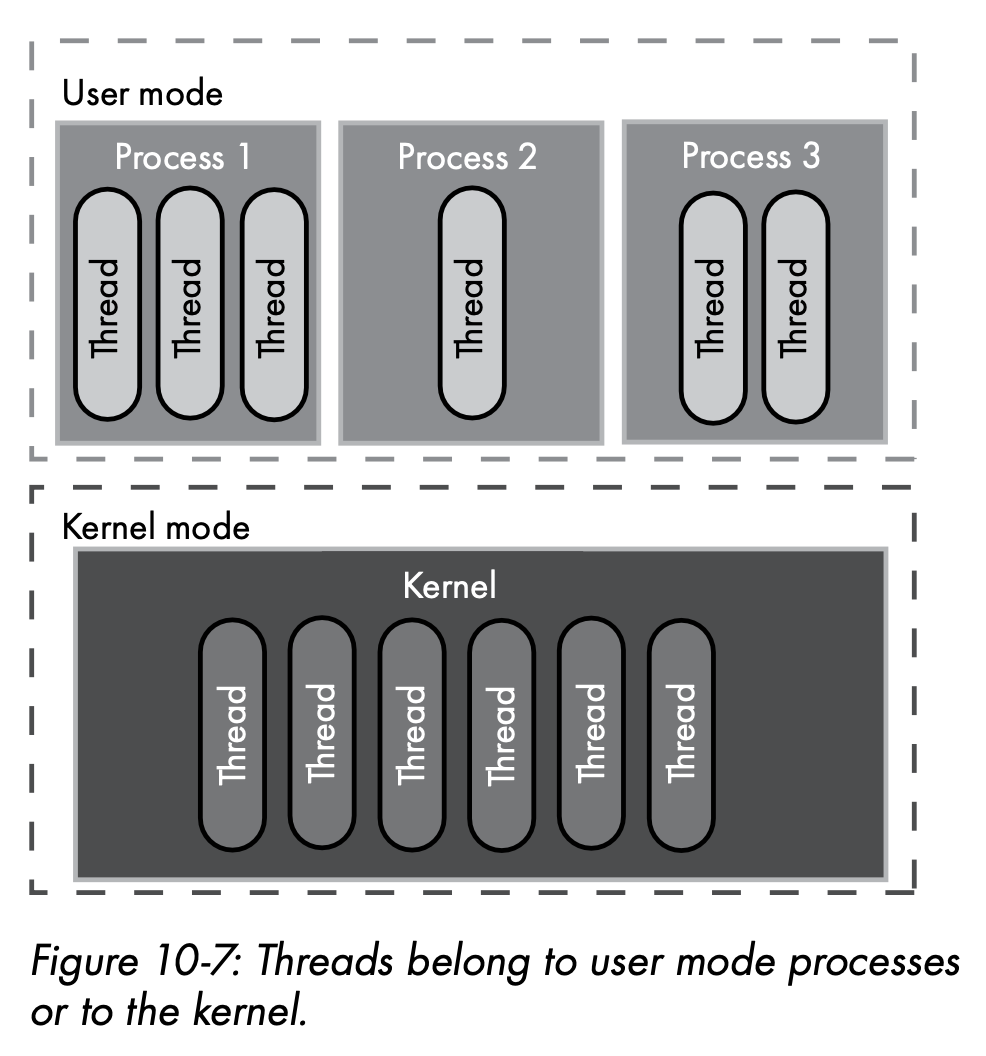
- Kernel mode v.s. User mode
Generally speaking, the kernel and many device drivers run in kernel mode, whereas everything else runs in user mode.
- Kernel mode
Code running in kernel mode has full access to the system, including access to all memory, I/O devices, and special CPU instructions.
- User mode
Code running in user mode has limited access... A process runs in a user mode bubble. It can do math, perform logic, access virtual memory, and control program flow, but it cannot interact directly with the outside world.
- System call
When user mode code requests that kernel mode code perform a privileged operation on its behalf, this is known as a system call.
- System call
- Kernel mode
- Process
A process is a container in which a program runs. This container includes a private virtual memory address space (more on this later), a copy of the program code loaded into memory, and other information about the state of the process.
- Memory space
- Physical memory (kernel mode)
Unlike user mode address space, kernel address space is shared by all code running in kernel mode. That means that any code running in kernel mode has access to everything in the kernel address space.
- Virtual memory (user mode)
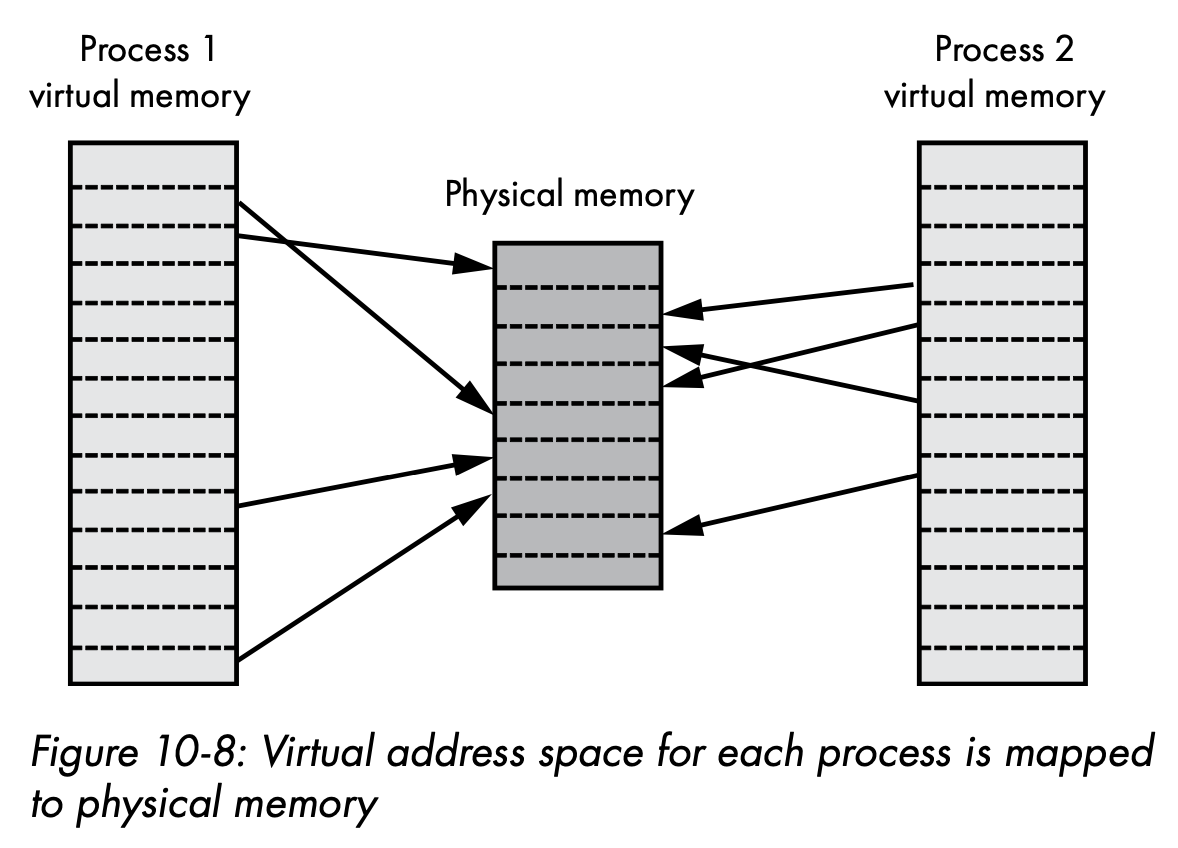
Operating systems do not grant user mode processes access to physical memory, and instead each process is presented with virtual memory—an abstraction that gives each process its own large, private address space.
- Physical memory (kernel mode)
- Threads
In Windows, ... a process object is a container, and threads belong to a process... In Linux, a group of threads that share an address space and have a common process identifier are considered a process.
- Memory space
- Scheduler
A thread gets a short period of time to run (known as a quantum), then the thread is suspended to allow another thread to run. Later, the first thread is scheduled again, and it picks up where it left off... developers write their multithreaded applications as if all their threads were running continuously in parallel.
- Kernel mode v.s. User mode
Part III: Internet
The internet
- TCP/IP model
- Stacks
- Link layer e.g. Wi-Fi, Ethernet
Link layer protocols provide a way to communicate on a local network.
- Media access control (MAC) address
- Internet layer e.g. IP
Internet layer protocols provide a mechanism for communicating across networks.
- IPv4 & IPv6
- Subnet
Computers connected to the same local network have IP addresses that begin with the same leading bits and are said to be on the same subnet... Computers that are on different subnets must send their traffic through a router, a device that connects subnets and operates at the internet layer.
- Subnet mask
- Transport layer e.g. TCP, UDP
Transport layer protocols provide a communications channel for applications to send and receive data between hosts.
- Port number
- Application layer e.g.HTTP, SSH, FTP, SMTP
Protocols that operate at the application layer provide application- specific functionality, such as sending an email or retrieving a web page.
- Link layer e.g. Wi-Fi, Ethernet
- Data
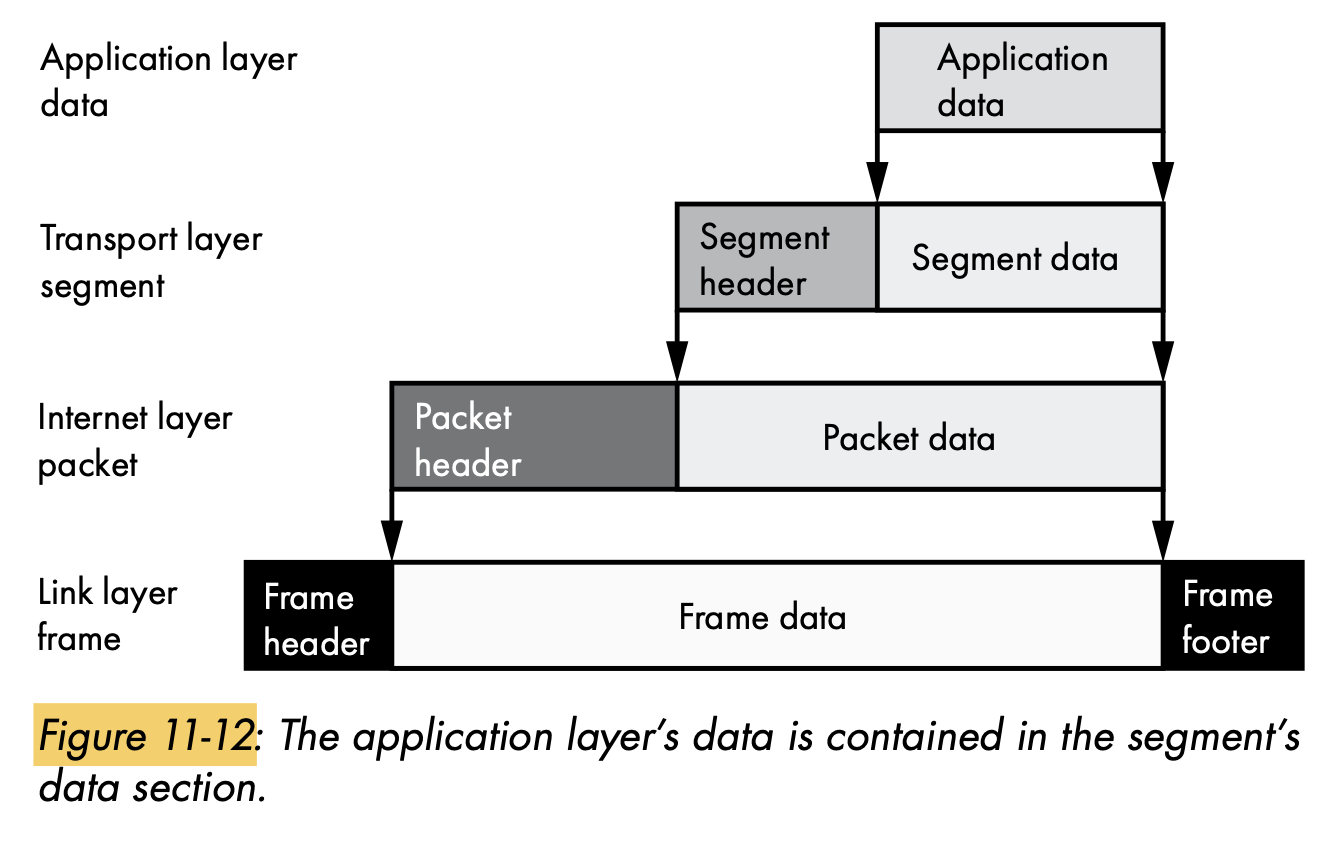
- Devices
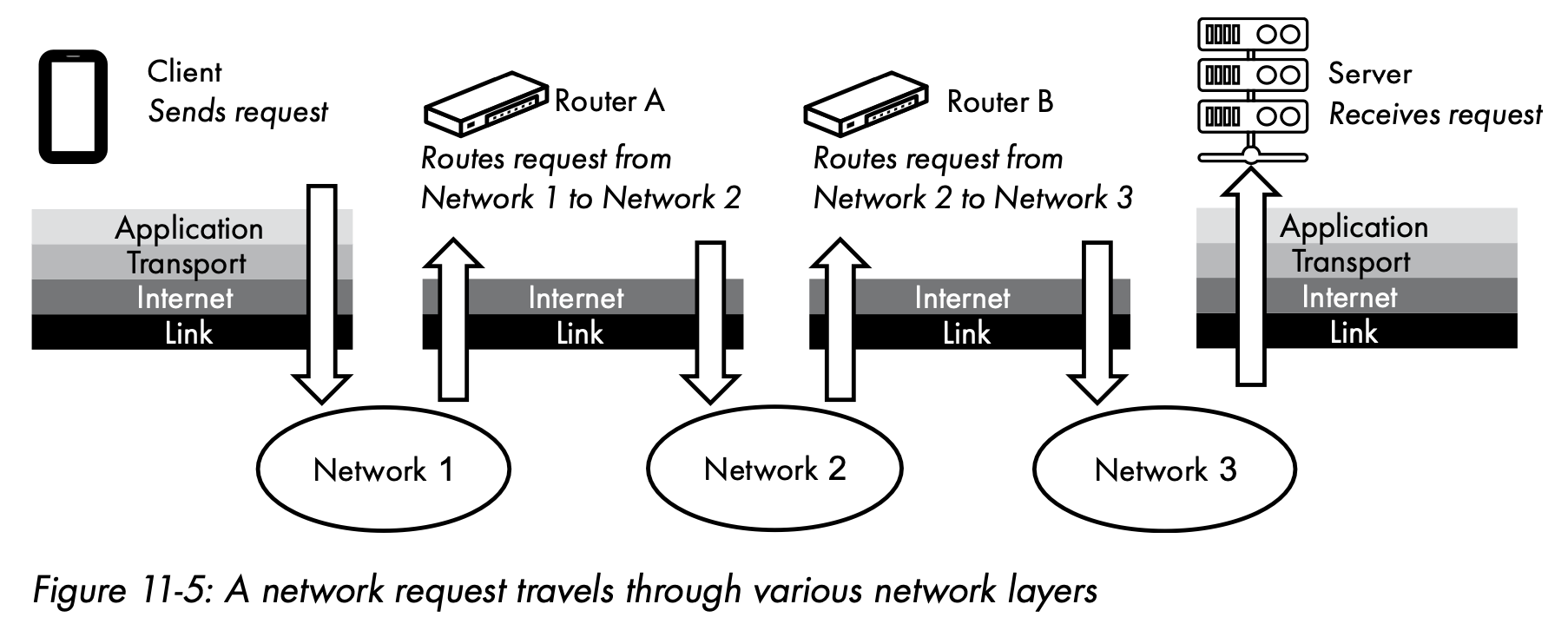
Although network hosts (such as a client or server) make use of protocols from all four layers, other types of networking hardware (such as switches and routers) only use protocols associated with lower layers. Such devices can perform their jobs without bothering to examine the higher layer protocol data contained in a network transmission.
- Stacks
- Foundational Internet capabilities
- Dynamic host configuration protocol (DHCP)
Most IP addresses are assigned dynamically using Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP)... When a device connects to a network, it broadcasts a message to discover any DHCP servers. A broadcast is a special kind of packet that’s addressed to all hosts on the local network.
- Private IP Addresses
Any address that matches the pattern of 10.x.x.x, 172.16.x.x, or 192.168.x.x is a private IP address... The catch is that private IP addresses are nonroutable—they can’t be used on the public internet. A DHCP server on a home network can assign these addresses without worrying about whether any other network is using the same addresses
- Network address translation (NAT)
Network Address Translation (NAT) allows devices on a private network, often a home network, to all use the same public IP address on the internet. As packets flow through a NAT router, the router modifies the IP address information in those packets.
- Private IP Addresses
- Domain name system (DNS)
- Resolving hostname
Software needs to be able to query DNS to convert hostnames to IP addresses—this is known as resolving a hostname—this is known as resolving a hostname. To enable this functionality, hosts are configured with a list of the IP addresses of DNS servers.
- DNS hierarchy
Each level has an associated DNS server(s) responding to queries. They work together to resolve the hostname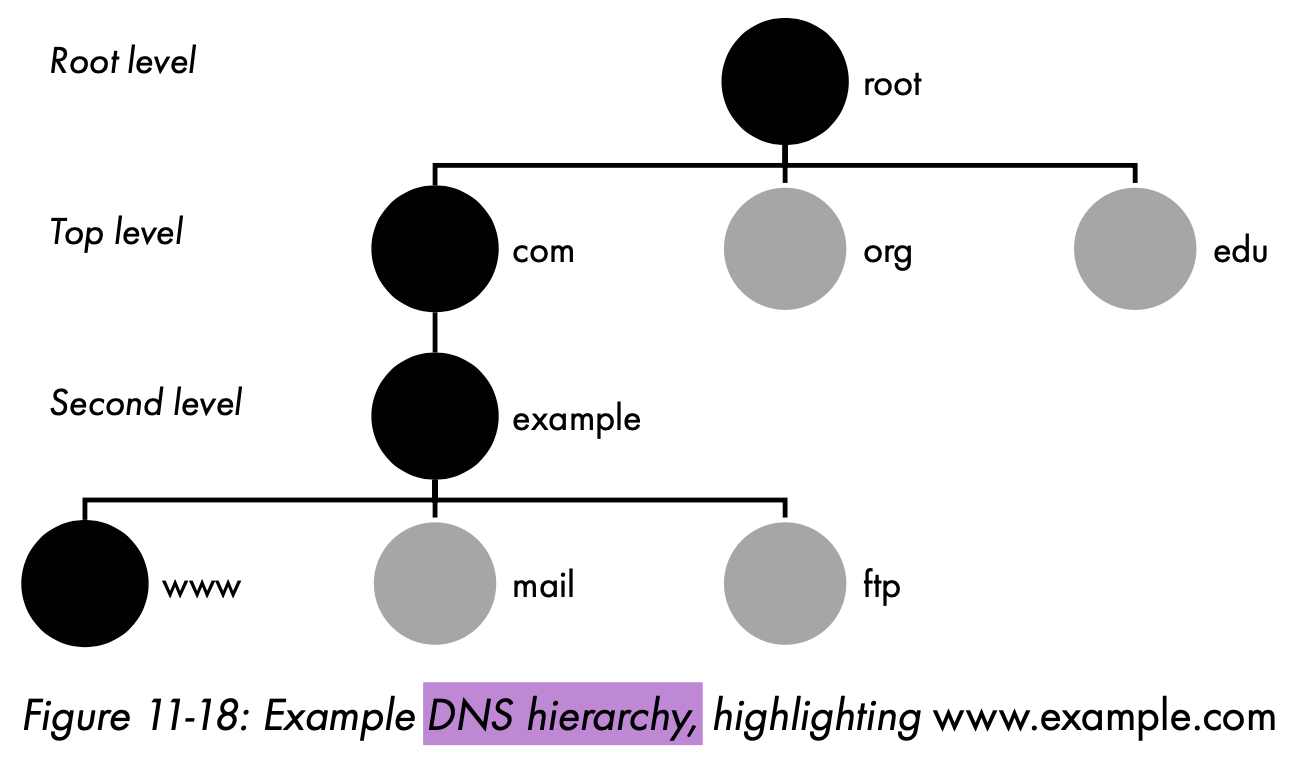
- Resolving hostname
- Dynamic host configuration protocol (DHCP)
The world wide net
- The world wide net
The World Wide Web, often just called the web, is a set of resources, delivered using HyperText Transfer Protocol (HTTP) over the internet.
- Distributed
- Addressable
Uniform resource locators (URLs) - Linked
- Searchable
- HTTP & HTTPS
When an HTTPS session begins, the client connects to the server with a client hello message with details of how it wishes to securely communicate. The server responds with a server hello message that confirms how the communication will occur. The server also sends a set of bytes known as a digital certificate, which includes the server’s public cryptographic key, used for asymmetric encryption. The client then checks if the server’s certificate is valid. If so, the client encrypts a string of bytes using the server’s public key and then sends the encrypted message to the server. The server decrypts the bytes using its private key. The server and client both use the information previously exchanged to compute a shared secret key, used for symmetric encryption. Once both client and server have the shared key, that key is used to encrypt and decrypt all communication between the client and server for the duration of the session.
- The Languages of the Web
- HyperText markup language (HTML)
- Other formats of web data
JSON & XML
- Other formats of web data
- Cascading style sheets (CSS)
- JavaScript
- HyperText markup language (HTML)
- Web browser
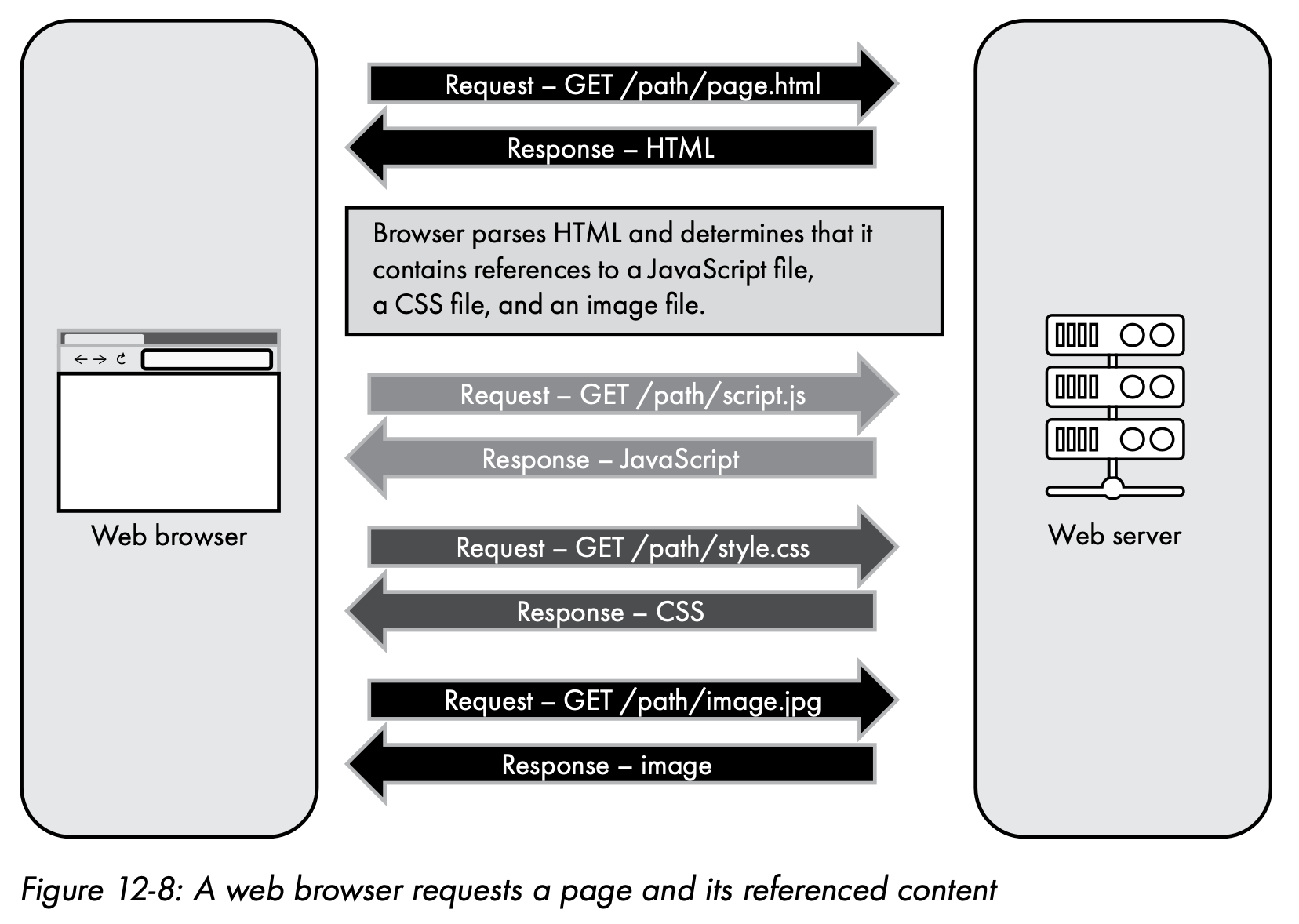
- Web server
- Dynamic website
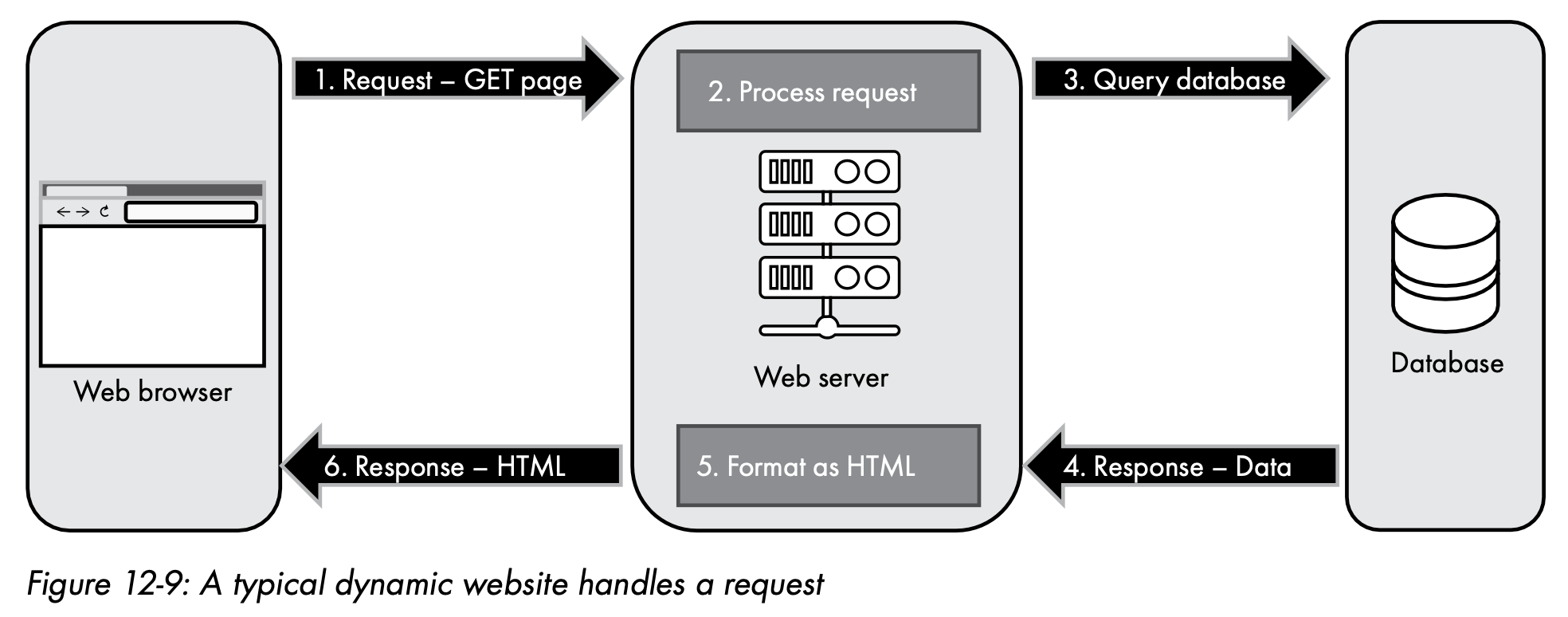
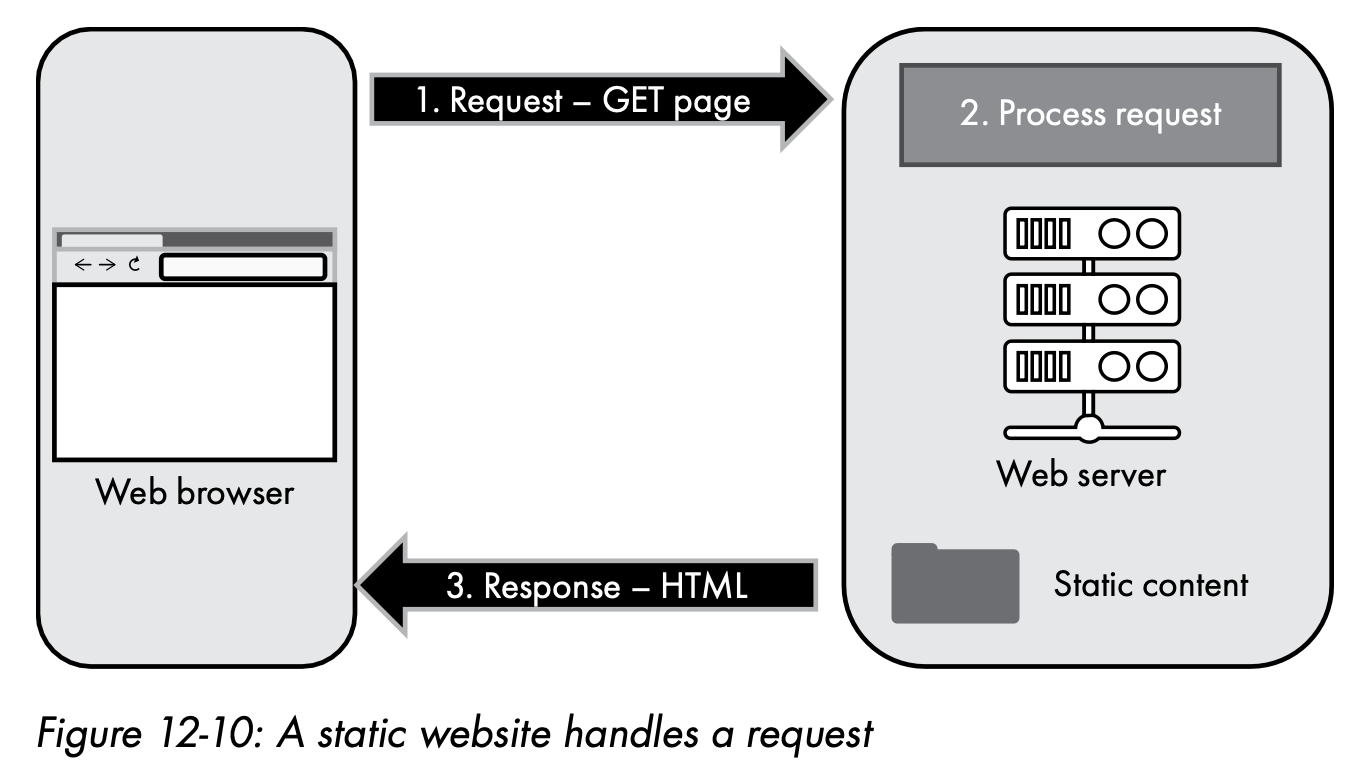
- Static website
- Dynamic website
The deep web & dark web
- Surface web
The surface web is indexed by search engines, and sometimes the surface web is defined as content that can be found with a search engine.
- Deep web
The deep web is web content that cannot be accessed without logging in to a website or web service.
- Dark web
The dark web is web content that requires specialized software to access. You cannot access the dark web using only a standard web browser.
Part IV: Modern Computing
App
- Native app
- Cross-platform framework
These cross-platform solutions abstract the underlying details of each operating system API, making it possible for developers to write code that can be built to run on multiple platforms.
- Cross-platform framework
- Web app
Progressive Web Apps (PWAs) offer a set of technologies and guidelines that help bridge the gap between native apps and web apps... If a website meets the criteria for a PWA, modern web browsers give users the option of adding an icon for the PWA to their home screen or desktop.
Virtualization & emulation
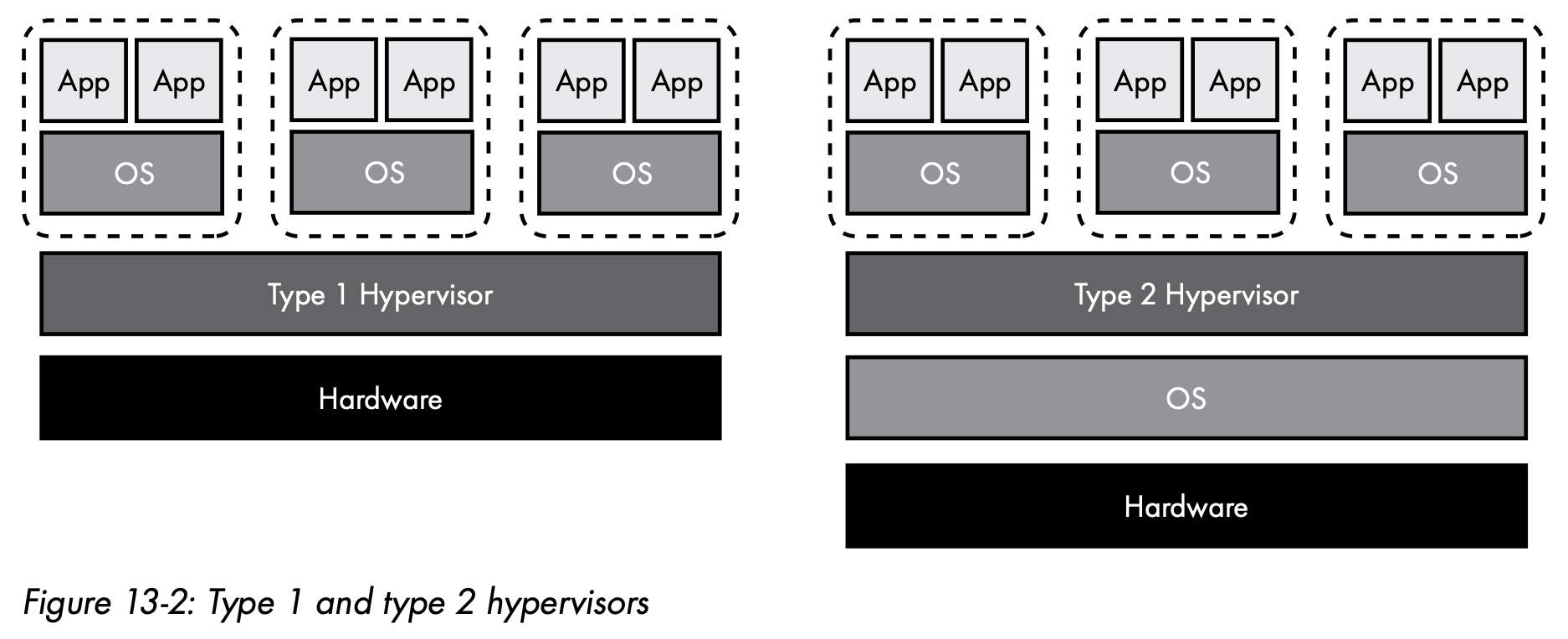
- Virtualization
For example, a computer running Windows can run an instance of Linux in a virtual machine. Virtual machines also allow data centers to host multiple virtual servers on a single physical server.
-
Hypervisor
-
Container
Unlike a virtual machine, a container shares a kernel with the host OS and with other containers running on the same computer... Containers provide the isolation of a VM without the overhead of running a separate kernel for each VM.
In general, containers are limited to running the same operating system as the host since the kernel is shared.
P.S. Docker Desktop for Windows/Mac uses a lightweight Linux VM (like WSL2 or Hyper-V) to run Linux containers under the hood, since macOS and Windows do not have a native Linux kernel.
-
- Emulation
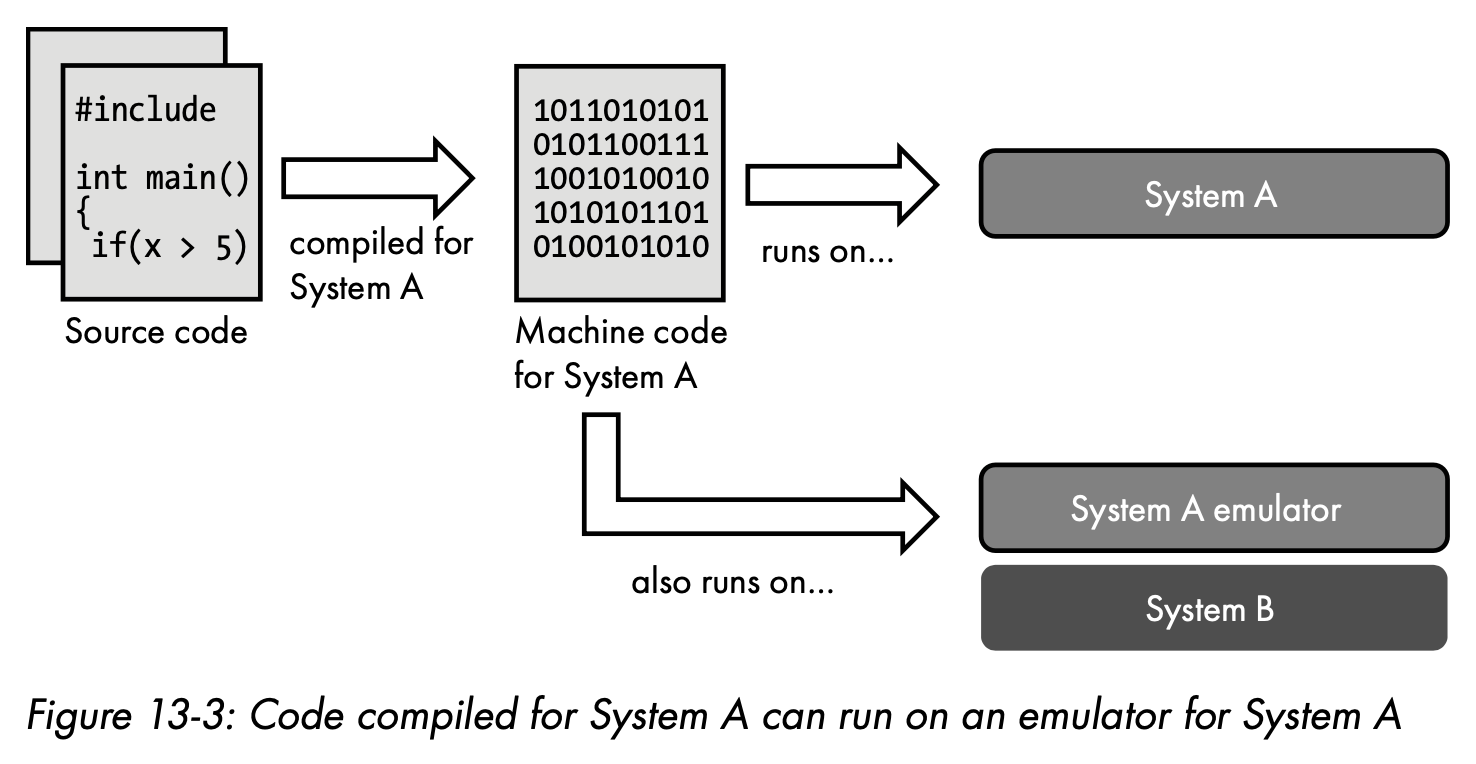
Emulation is the use of software to make one type of device behave like another type of device. Emulation and virtualization are similar in that they both provide a virtual environment for running software, but whereas virtualization offers up a slice of the underlying hardware, emulation presents virtual hardware that’s unlike the physical hardware in use.
Cloud computing
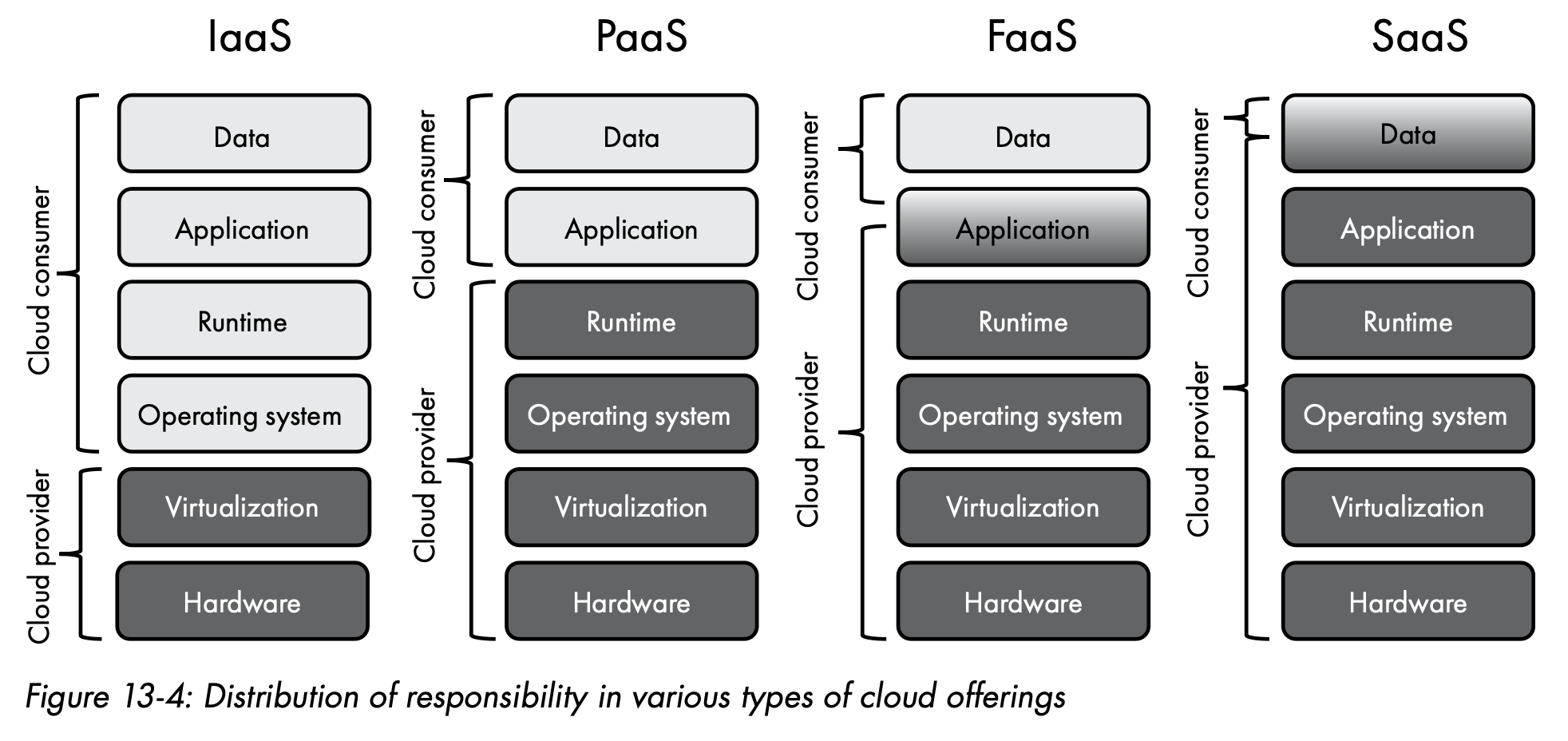
- Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS)
- Platform as a Service (PaaS)
- Function as a Service (FaaS)
- Software as a Service (SaaS)
e.g. Microsoft 365, Google G Suite, & Dropbox
Bitcoin
- Block chain
Encryption and decryption are employed to ensure the integrity of transactions and prevent tampering with the data in the blockchain. Once written, blockchain data is immutable—it can’t be changed.
- Cryptocurrency
A cryptocurrency is a digital asset intended to be used for financial transactions, as a substitute for a traditional currency like the US dollar... Unlike traditional currencies, cryptocurrencies are typically decentralized, with no single organization controlling their use.
- Bitcoin wallets
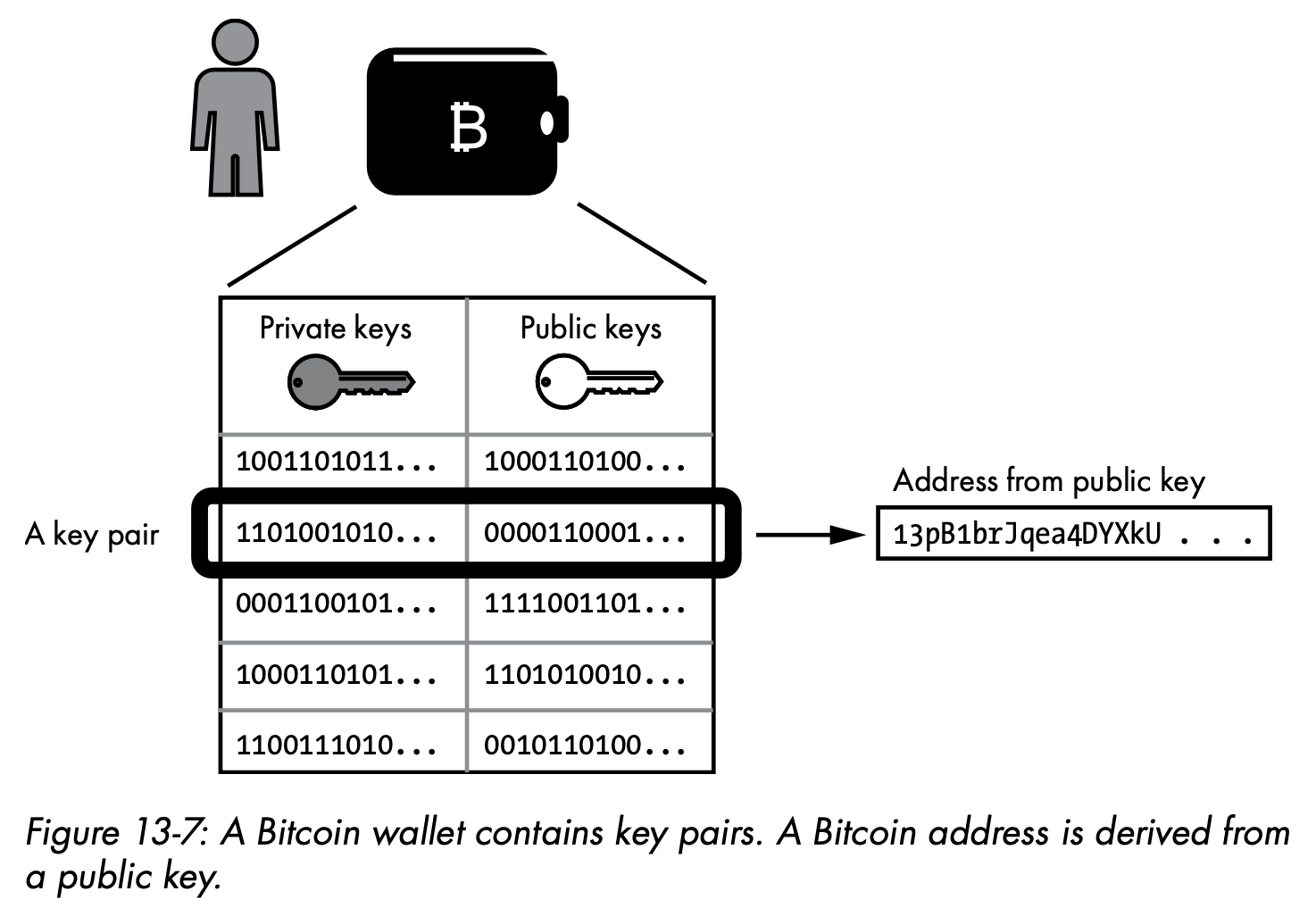
- Transaction
To send bitcoins, wallet software constructs a transaction specifying the details of the transfer, digitally signs it with a private key, and broadcasts the transaction to the Bitcoin network. The computers in the Bitcoin network verify the transaction and add it to a new block on the blockchain.
- Bitcoin mining
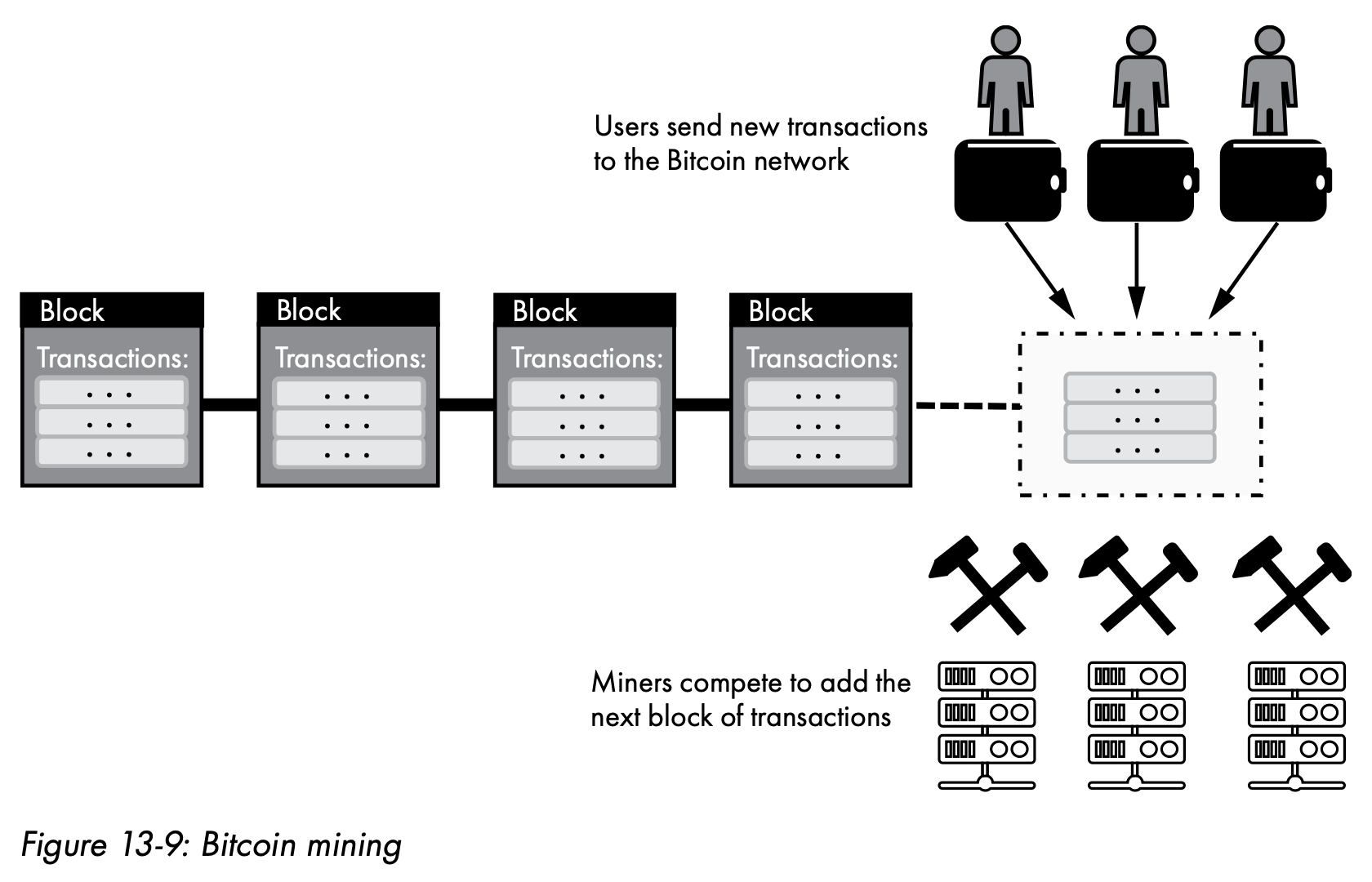
In order to add a block of transactions to the blockchain, a miner must verify the transactions included in the block (ensuring that each transaction is syntactically correct, that the input coins haven’t already been spent, and so forth), and it must also complete a computationally difficult problem.-
Proof of work
Requiring miners to solve such a problem prevents tampering with the blockchain, since altering a block would require solving the problem for the altered block and for every block that comes after it in the blockchain.
-
Reward
The first miner to complete the problem is awarded a sum of bitcoins. This is how new bitcoins are generated and introduced into the system.
P.S. The miner also receives a fee from the transactions. After 21 M coins been mined, there won't be any new coins and the fee will be the only reward.
-
- Bitcoin wallets
VR & AR & XR
VR and AR are referred to together as XR.
- Virtual reality (VR)
- 3 DoF
Allow users to look around - 6 DoF
Allow users to move around
- 3 DoF
- Augmented reality (AR)
While VR attempts to completely immerse the user in a virtual world, AR overlays virtual elements onto the real world.
IoT
In recent years we’ve seen the growth of new types of devices connecting to the internet—speakers, televisions, thermostats, doorbells, cars, lightbulbs, you name it! This concept of connecting all kinds of devices to the internet is known as the Internet of Things (IoT).
Challenges:
- Security
Even if the data on the device isn’t of interest to an attacker, the device can act as a foothold in an otherwise well- defended network, or it can be used as a launch point for a remote attack against a different target.
- Privacy
- Functionality
Dependent on the availability of networks and cloud services